前言
Phoenix是构建在HBase上的一个SQL层,能让我们用标准的JDBC APIs而不是HBase客户端APIs来创建表,插入数据和对HBase数据进行查询。
Phoenix完全使用Java编写,作为HBase内嵌的JDBC驱动。Phoenix查询引擎会将SQL查询转换为一个或多个HBase扫描,并编排执行以生成标准的JDBC结果集。
直接使用HBase API、协同处理器与自定义过滤器,对于简单查询来说,其性能量级是毫秒,对于百万级别的行数来说,其性能量级是秒。
Phoenix通过以下方式使我们可以少写代码,并且性能比我们自己写代码更好:
将SQL编译成原生的HBase scans。
确定scan关键字的最佳开始和结束让scan并行执行
本文使用 HBase2.1.10 + Phoenix5.1.2
Phoenix安装
下载与安装
http://archive.apache.org/dist/phoenix/phoenix-5.1.2/
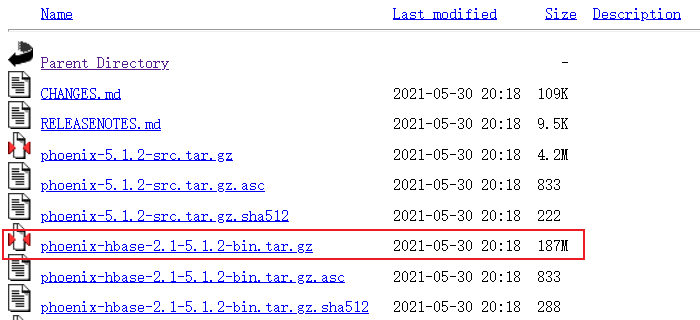
解压
1 | tar -zxvf phoenix-hbase-2.1-5.1.2-bin.tar.gz -C /data/tools/bigdata/ |
环境变量
环境变量
1 | cd /etc/profile.d/ |
创建配置文件
1 | vi /etc/profile.d/phoenix.sh |
内容设置为
1 | # phoenix |
配置生效
1 | source /etc/profile |
查看是否生效
1 | cd $PHOENIX_HOME |
配置
Phoenix用来连接Hbase,不用做分布式部署。
把Jar复制到Hbase里
1 | cd $PHOENIX_HOME |
注意不要复制phoenix-pherf-5.1.2.jar这个Jar包,会导致重复而无法启动Hbase。
查看是否复制成功
1 | cd $HBASE_HOME/lib/ |
Hbase配置添加
1 | vi $HBASE_HOME/conf/hbase-site.xml |
添加
1 | <!-- Phoenix 支持HBase 命名空间映射 --> |
配置文件软连接
1 | cd $PHOENIX_HOME |
同步分发Hbase Phoenix不用分发
1 | ha-fenfa.sh $HBASE_HOME |
运行
查看所有服务
1 | ha-call.sh "jps" |
停止Hbase
1 | $HBASE_HOME/bin/stop-hbase.sh |
如果哪个节点没有停止,我们手动停止
1 | ssh hadoop01 "hbase-daemon.sh stop regionserver" |
清除zookeeper 信息
1 | zkCli.sh -server hadoop01:2181 <<< "deleteall /hbase" |
清除HDFS 数据
1 | hadoop fs -rm -r /hbase |
/hbase来自于hbase的配置文件中
启动Hbase
1 | $HBASE_HOME/bin/start-hbase.sh |
Phoenix Shell操作
连接
连接phoenix客户端
1 | sqlline.py hadoop01,hadoop02,hadoop03:2181 |
第一次启动比较慢,请耐心等待。
查询
1 | !tables |
Schema的操作
1)创建schema
默认情况下,在phoenix中不能直接创建schema。
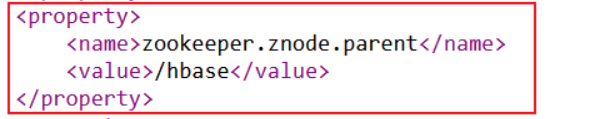
需要将如下的参数添加到Hbase中conf目录下的hbase-site.xml 和 phoenix中bin目录下的 hbase-site.xml中
1 | <property> |
重新启动Hbase和
1 | stop-hbase.sh |
查看所有schema
1 | !schema |
创建schema
1 | create schema "zdb"; |
注意:在phoenix中,schema名,表名,字段名等会自动转换为大写,若要小写,使用双引号,如
"zdb"。
执行如下命令使用这个新建的 schema:
1 | use "zdb"; |
执行如下命令则使用默认的 schema:
1 | USE DEFAULT; |
执行如下命令可以删除 zdb 这个 schema:
注意:确保该 schema 下的表都已删除,否则该 schema 会删除失败。
1 | DROP SCHEMA "zdb"; |
SQL语法
显示所有表
1 | !table |
创建表
创建表的时候一定要设置主键,这个会作为RowKey使用。
直接指定单个列作为RowKey
1 | CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS "tuser"( |
指定多个列的联合作为RowKey
1 | CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS us_population ( |
插入数据
1 | upsert into "tuser" values('1001','zhangsan','beijing'); |
查询记录
1 | select * from "tuser"; |
分页查询
1 | select * from "tuser" order by id desc limit 1 offset 0; |
其中
limit取多少条offset从多少条开始
在Hbase中查看
1 | hbase shell |
索引
查看是否用到索引
1 | explain select * from "tuser"; |
只要出现FULL SCAN就证明没用用到索引
创建索引
1 | CREATE INDEX "index_tuser_name" ON "zdb"."tuser"(name); |
删除索引
1 | DROP INDEX "index_tuser_name" ON "zdb"."tuser"; |
如果创建二级索引报错
Mutable secondary indexes must have the hbase.regionserver.wal.codec property
停止hbase
1 | $HBASE_HOME/bin/stop-hbase.sh |
在每个regionServer的hbase-site.xml添加以下语句:
1 | <property> |
分发配置
1 | ha-call.sh "rm -rf $HBASE_HOME/logs/*" |
重启hbase即可
1 | $HBASE_HOME/bin/start-hbase.sh |
也要重启queryserver
1 | queryserver.py stop |
删除记录
1 | delete from "tuser" where id='1001'; |
删除表
1 | drop table "tuser"; |
7)退出命令行
1 | !quit |
表的映射
默认情况下:
Phoenix中创建的表在HBase中是可以看到的。
直接在HBase中创建的表,通过Phoenix是查看不到的。
1)表的关系
如果要在Phoenix中操作直接在HBase中创建的表,则需要在Phoenix中进行表的映射。
映射方式有两种:
- 视图映射
- 表映射。
2)命令行中创建表test
HBase 中test的表结构如下,两个列族info1、info2。
| Rowkey | info1 | info2 |
|---|---|---|
| id | name | address |
启动HBase Shell
1 | hbase shell |
创建HBase表test
1 | create 'test','info1','info2' |
3)视图映射
Phoenix创建的视图是只读的,所以只能用来做查询,无法通过视图对源数据进行修改等操作。
在phoenix中创建关联test表的视图
1 | create view "test"(id varchar primary key,"info1"."name" varchar, "info2"."address" varchar); |
删除视图
1 | drop view "test"; |
4)表映射
使用Apache Phoenix创建对HBase的表映射,有两种方法:
- HBase中不存在表时,可以直接使用create table指令创建需要的表,系统将会自动在Phoenix和HBase中创建同名的表,并会根据指令内的参数对表结构进行初始化。
- 当HBase中已经存在表时,可以以类似创建视图的方式创建关联表,只需要将create table改为create view即可。
1 | create table "test"(id varchar primary key,"info1"."name" varchar, "info2"."address" varchar) column_encoded_bytes=0; |
表映射中数值类型的问题
Hbase中存储数值类型的值(如int,long等)会按照正常数字的补码进行存储. 而phoenix对数字的存储做了特殊的处理. phoenix 为了解决遇到正负数同时存在时,导致负数排到了正数的后面(负数高位为1,正数高位为0,字典序0 < 1)的问题。
phoenix在存储数字时会对高位进行转换.原来为1,转换为0, 原来为0,转换为1.
因此,如果hbase表中的数据的写是由phoenix写入的,不会出现问题,因为对数字的编解码都是phoenix来负责。
如果hbase表中的数据不是由phoenix写入的,数字的编码由hbase负责. 而phoenix读数据时要对数字进行解码。 因为编解码方式不一致。导致数字出错。
1) 在hbase中创建表,并插入数值类型的数据
1 | create 'person','info' |
注意: 如果要插入数字类型,需要通过Bytes.toBytes(123456)来实现。
2)在phoenix中创建映射表并查询数据
1 | create table "person"(id varchar primary key,"info"."salary" integer) column_encoded_bytes=0; |
会发现数字显示有问题
3) 解决办法:
在phoenix中创建表时使用无符号的数值类型unsigned_long
1 | create table "person"(id varchar primary key,"info"."salary" unsigned_long) column_encoded_bytes=0; |
Phoenix Query Server
注意
使用胖客户端不需要安装这个,只有使用瘦客户端的时候才要安装。
在 4.4-4.14 和5.0 releases 中 query server 及其 JDBC client 是内置的.
4.15以后 及5.1 release版本,Phoenix Query Server 需要单独下载, 版本号为 6.0.
下载及安装
下载地址:Download page
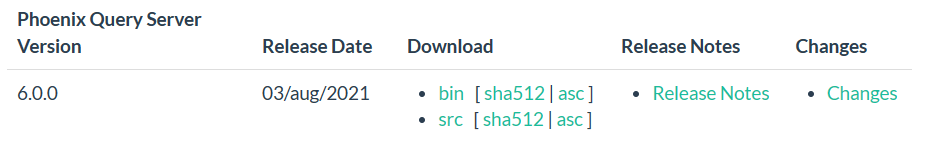
1 | tar -zxvf phoenix-queryserver-6.0.0-bin.tar.gz -C /root/ |
启动query server
1 | queryserver.py start |
测试
1 | sqlline-thin.py http://hadoop01:8765 |
停止
1 | queryserver.py stop |