管理员运行
注意
如果应用没有使用管理员身份运行,会导致应用更新被阻拦,无法更新。
步骤
1.打开项目的属性
2.选择“安全性”,勾选启用ClickOnce安全设置
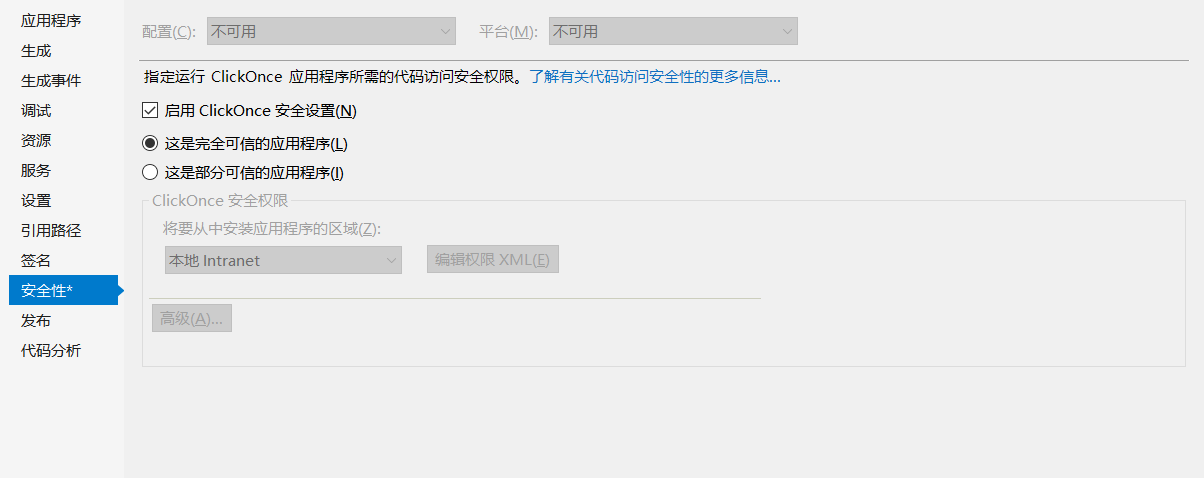
3.然后会在Properties里自动生成 app.manifest
打开app.manifest中修改为如下配置
1 | <requestedPrivileges xmlns="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:asm.v3"> |
可用设置
1 | <requestedExecutionLevel level="asInvoker" uiAccess="false" /> |
4.如果现在直接运行会报错
所以要在之前的属性里取消勾选启用ClickOnce安全设置。
现在运行程序就会要求以管理员身份运行了。
注意
尽管程序的默认用户账户控制是
asInvoker,在以管理员身份运行的vs里对其他程序的调用也会以管理员身份(以当前调用权限运行)。
代码形式
1 | using System; |
判断程序是否以管理员运行
1 | using System.Security.Principal; |
注册表写入
1 |
|